ASR2014 Thermodynamics of the Refrigeration Circuit Teaching Equipment Fridge Training Equipment
Learning Objectives / Experiments
– cyclic process in the log p-h diagram
– comparison of the real cyclic process and the ideal cyclic process
– energy balances at the evaporator and condenser
– calculation of the motor power via speed and torque
– determination of losses
– calculation of the coefficient of performance
– operating behaviour under load
– non-steady-state operating behaviour
Specification
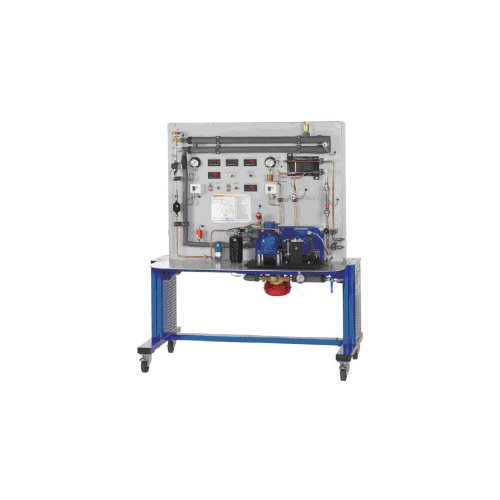
[1] thermodynamic investigation of a refrigeration circuit
[2] refrigeration circuit with open compressor, watercooled condenser, thermostatic expansion valve and indirectly heated evaporator
[3] compressor drive with speed-controlled motor via V-belt
[4] motor on pendulum bearing for torque measurement
[5] tube evaporator with hot water circuit as cooling load
[6] water-cooled coaxial coil heat exchanger as condenser
[7] displays for temperature, pressure, flow rate, speed, torque and power at the equipment
[8] software for data acquisition via USB under Windows Vista or Windows 7
[9] refrigerant AR134a, CFC-free
Technical Data
Open compressor
– refrigeration capacity: approx. 550W (at a speed
of 500min-1 and -10/20°C)
– motor: 550W, 1.400min-1
Heater: 1x 1.000W
Condenser
– capacity: 1.300W
Measuring ranges
– temperature: 9x -30…100°C, 1x 0…100°C
– pressure: 1x -1…9bar, 1x -1…24bar, 2x -1…15bar
– torque (compressor): 0…10Nm
– speed (compressor): 0…2.500min-1
– power consumption (compressor): 0…1.125W
– power (heater): 0…1.125W
– flow rate (water): 5…70g/s
– flow rate (refrigerant): 0…0,5L/min
Dimensions and Weight
LxWxH: 1.520x790x1.760mm
Weight: approx. 120kg
Required for Operation
230V, 50/60Hz, 1 phase
Water connection