AZM9150 Pneumatic Transport Teaching Equipment Fluid Mechanics Experiment Equipment
1.Product Overview
1.1 Product Introduction
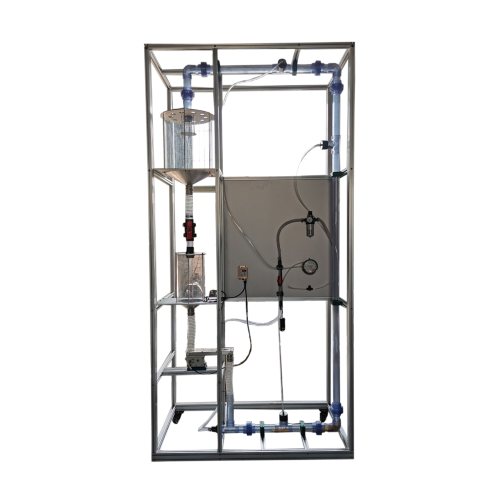
The pneumatic conveying device can be used to convey the dispersed solids in the pipeline.
The solids are transported to an air flow feed tank through a vibrating tank, and the air flow transports the solids to the pipe, and the transportation in the collection tank is terminated.
Depending on the speed of the air flow and the solids content, different transport conditions may occur. At high speeds, the solids are dispersed in a tube of uniform cross-section (dilute phase transport). If the speed is reduced, the solid particles will slide down due to their higher settling speed. The particles disintegrate again in the air flow and reduce the speed, reducing the settling speed of the individual particles, which eventually leads to blockage and transportation. Through the transparent tube, different transportation states can be observed.
To determine the pressure loss and flow rate, the measurement point is set at the relevant location. The air speed is adjusted by a pressure regulator. The flow of solid particles can be adjusted by the vibration feed controller. Compressed air must be provided from the laboratory.
1.2 Features
The main body of the experimental device is built with high-strength industrial aluminum profiles, and a universal wheel with brake is installed at the bottom to facilitate movement and fixation. The pipeline is made of transparent material, which is convenient for observing the trajectory of solid particles.
1.3 Performance parameters
Vertical tube
Height: 2m
Diameter: 50mm
Feeding barrel volume: 12L
Receiving barrel volume: 38L
Compressed air: minimum 2bar and 60m³ / hour
Power supply: AAC220V 10A
1.4 practical training items that can be completed
Operation of pneumatic conveying system
Observation of different transportation states
Measurement of air velocity
- Experimental content
2.1 Operation experiment of gas delivery system
2.2 Observation experiment of different transportation states
2.3 Measurement of air velocity
2.4 Solid particle feeding speed experiment