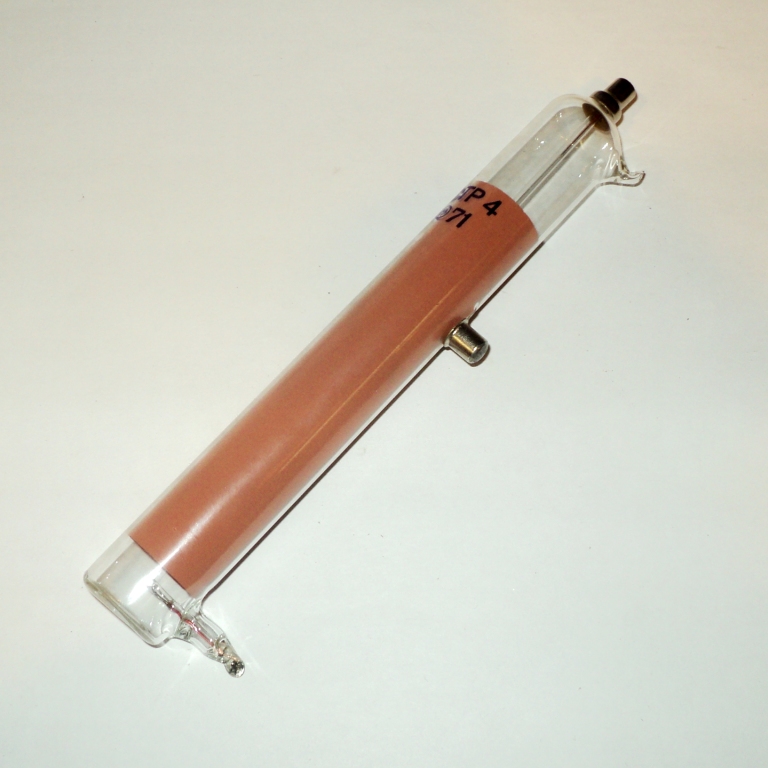
X-ray radiation counter.
The name of the MSTR stands for:
M — copper cathode;
C — self-
extinguishing counter;
T — end window;
P — for X-ray diffraction
or X-ray spectral studies.
Platinum content in one device: 0.02213 grams.
Main technical data:
The maximum length is 180 mm.
The maximum width is 40 mm.
The voltage of the beginning of the count: the lowest 1200 V, the highest 1350 V.
The counting speed corresponding to normal operation (the highest) is -25,000 imp/min.
The length of the plateau of the counting characteristic (the smallest) is 200 V.
The slope of the plateau of the counting characteristic (the largest) is 0.05%/V.
The surface density of mica of the entrance window (the highest) is 5.9 mg/cm2.
Normal working conditions:
Load resistance — 8 -15 Mohm.
The parasitic capacitance of the input circuit of the counting and measuring device (the largest) is 25 pf.
Permissible fluctuations in ambient temperature from +5 to +35 ° C.
which the space between the electrodes is filled with some gas.
Depending on the electric field strength in the gas gap and
its distribution, these detectors have different properties. Thus, with
a relatively low electric field strength, the current flowing in
an electric circuit does not depend on the voltage on the capacitor and is equal
to the product of the electron charge by the number of ion pairs that occur per
unit time in the volume of the capacitor. Such detectors are called
ionization chambers. At higher values of the field strength, as a
result of secondary ionization
, the primary ionization effect increases. In this case , the current depends on the voltage at
It is proportional to the ionization effect created by radiation.
Such detectors are called proportional counters.
Finally, at even higher values of the field strength
, an independent discharge occurs in the capacitor if a
charged particle enters the detector volume. Such detectors are called gas discharge
meters.