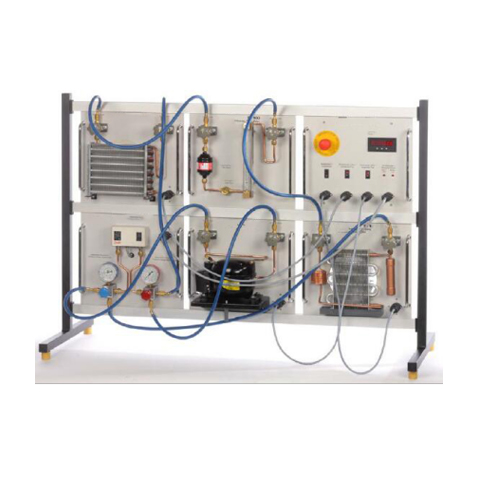
ASR2040 Introduction to Refrigeration Teaching Equipment Refrigerator Training Equipment
Learning Objectives / Experiments
Fundamentals of a simple refrigeration circuit
– Detect and understand the cyclic process
– Changes of state of the refrigerant
– Represent the refrigeration circuit in the process schematic
– Representation of the cyclic process in the log p-h diagram
– Estimate key figures, refrigeration capacity and heat flows
Different operating modes
– Cool air
– Generate cold water
– Heat pump (generate hot water)
Practical exercises
– Drain and fill refrigeration system
– Fault finding
Specification
[1] Set-up of simple refrigeration circuits with different components
[2] 8 self-contained operational modules mounted on a plate each
[3] Light-weight aluminium frame to arrange 6 modules
[4] Evaporator and condenser each available as air/refrigerant heat exchanger (finned tube heat exchanger) and as water/refrigerant heat exchanger (with pipe coil)
[5] Modules fitted with manual valves
[6] Components connected via hoses
[7] CFC-free refrigerant AR134a
Technical Data
Hermetic refrigerant compressor
– power consumption: 67W at -10/32°C
– refrigeration capacity: 151W at 5/32°C
Tank content
– water tank, evaporator: 2L
– water tank, condenser: 3L
Pressure switch activation pressure
– LP: 1bar
– HP: 14bar
Manometer
– intake pressure: 1…10bar
– delivery pressure: 1…30bar
Rotameter: 0.4…7.4L/h
Dimensions and Weight
l x w x h: 1300x700x900mm
l x w: 370x340mm (component plates)
Weight: approx. 30kg
Connections
230V, 50/60Hz, 1 phase or 120V, 60Hz/CSA, 1 phase