ATB221018AS04 Anaerobic digester Didactic Equipment Hydrodynamics Experiment Apparatus
INTRODUCTION
Anaerobic digestion (also known as methane fermentation) is a biological process that takes place naturally. In this process certain microorganisms break biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. Biogas obtained in this process is a new energy source used in as a useful mean of decontamination and as an alternate source of renewable energy.
Biogas generation through anaerobic breakdown is considered useful when treating biodegradable residues, since it generates valuable fuel, as well as an effluent that can be applied as a soil conditioning substance or generic fertilizer
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
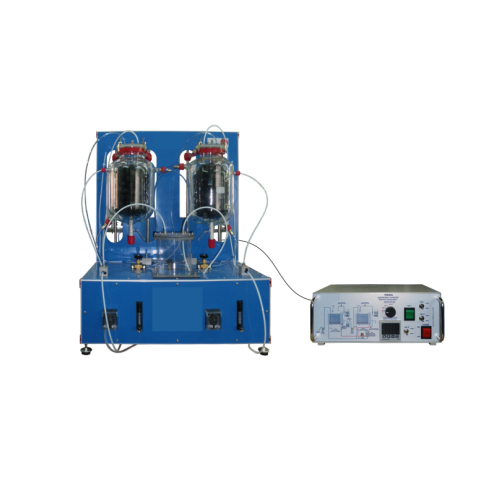
The objective of the Anaerobic Digester, is to study and understand the stages of the anaerobic digestion, as well as the anaerobic digestion process itself. It is supplied with two packed anaerobic digesters. In this way, the user can work either in only one stage or in two stages, separating the different phases of the digestion process (the processes of hydrolysis, acidogenesis and acetogenesis would take place in the first digester, and the methanogenesis in the second digester).
Both digesters have a heating water circuit with valves to regulate the appropriate temperature in each part of the process and the operation with different ranges depending on the microorganisms used. Thus, it can operate at the psychrophilic range (room temperature), mesophilic range (temperatures around 35 °C) or thermophilic range (temperatures around 55 °C). The heating system of the digesters consists in making hot water from a thermostatic bath flow through the jacket of the reactor.
The unit has two peristaltic pumps to impel the supply to be introduced in the digesters. When working with a two-stage anaerobic digestion, one of the pumps carries the product from one of the digesters to the other, passing through a buffer tank, which collects the excess of flow from the first reactor. Two flowmeters measure the working flows.
Two volumetric tanks are also included for the storage and volume measurement of the generated biogas. The generated biogas flows through a pipe from the upper side of the digesters to these tanks, where the biogas volume is measured by means of a water displacement.
Such tanks have two parts: the upper side is where the generated biogas is collected and the second part, smaller than the first one and located below it, is used to collect the displaced water.
SPECIFICATIONS
Bench-top unit.
Anodized aluminum frame and panels made of painted steel.
Main metallic elements made of stainless steel.
Diagram in the front panel with distribution of the elements similar to the real one.
Two packed bed reactors (Anaerobic digesters) that may be operated in series or parallel flow arrangement:
Capacity: 5 l.
Heating jacket.
Reactor packing: 25 mm diameter BioBalls.
Two feed peristaltic pumps.
Water circulation pump of the thermostatic bath.
Thermostatic bath up to 60 ºC.
Two volumetric tanks to measure and store the volume of gas generated.
Damping vessel, capacity: 1 l.
Two water flow meter; range: 0 – 50 cm³/min.
Five temperature sensors “J” type.
Electronic Console:
Metallic box.
Temperature sensors connections.
Digital display for temperature sensors.
Selector for temperature sensors.
Pumps switches.
Thermostatic bath switch.
Main switch.
Cables and Accessories, for normal operation.
Dimensions:
Unit: 1000 x 800 x 1000 mm approx.
(39.36 x 31.49 x 39.36 inches approx.)
Weight: 50 Kg approx. (110 pounds approx.)
Electronic console: 300 x 230 x 135 mm approx.
(11.81 x 9.05 x 5.31 inches approx.).
Weight: 2 Kg approx. (4.4 pounds approx.)